Papilloma - Benign tumor formation of the skin and mucous membranes of viral etiology.It has the appearance of a papilla in a narrow base (leg), soft or dense consistency, from light color to dark brown.The location of papillomas in the skin leads to the formation of a cosmetic defect, in breathing, the voice of the larynx, the voice, in the mucous membrane of the internal organs: ulcerations and bleeding.The relapses of the disease are possible, the most formidable complication is malignant degeneration.Papill elimination can be carried out by electrocoagulation, crio -writing, surgical split, radio wave or laser exposure method.
General Information
Papillomas - This is a disease that affects epithelial cells and skin.The cause of papillomas is human papilloma, which belongs to the Papoviridae family, the papilloma group.Between HPV, viruses are distinguished with high and low oncogenic risk.The oncogenicity of papillomas is explained by the virus's ability to integrate their DNA into the human cell genome.
The infection mechanism with the human papillomavirus
Once in the human body, in the initial stage, HPV affects the basal cells of the epithelium.The microtrauma, scratches, cracks and other skin damage contribute to the penetration of papillomavirus in the body.For a long time, the virus can multiply mainly, not manifest clinically (chronic car).If the virus spreads in the surface layers of the skin, then over time, even with chronic papillomavirus transport, cell hyperplasia is observed.
Since the human papillomavirus is nested in the external environment, the infection occurs with direct contacts.Forced sexual ties lead to infection;Smoking, pregnancy, endometriosis, vitamin deficiency, immunodeficiencies are predisposing factors for infection to interact with the virus.The risk of infection increases with frequent contacts with naked human skin, for example, with massage.
Clinical manifestations of papillomas
Papilloma is a neoplasm of the skin or mucous membranes and seems papillary growth that stands out on the surrounding tissue.Papillomas are located on the skin, mucous membranes, in the inguinal region and in the genitals, in some cases, papillomas are found in the renal pelvis and in the mucous membrane of the urearies.
Since the papilloma consists of leather -covered connective tissue and contains blood vessels, bleeding is possible during trauma.Neoplasia grows up in the form of dispersed papillae in several directions and seems cauliflower.
The skin of the skin may not change, but in most cases papillomas have white to dirty brown.Favorite location: The skin of brushes and hands.In patients with immunodeficiencies, papillomatosis is widespread.The primary changes in the skin begin to appear 1-6 months after infection.The concentration of the virus in the affected areas reaches the maximum in the sixth month from the time of infection, this period is the most contagious.
Depending on the type of virus, the clinical manifestations of papillomas are variable.Then, vulgar papillomas are seen in the form of solid protuberance with a diameter of 1 mm with a rough keratinization surface.Vulgar papillomas are prone to fusion and, therefore, often affect significant skin areas.Simple (vulgar) papillomas are located everywhere, but are most often affected by the skin of the fingers and the back of Las Palmas.In children, especially young people are affected by papillomas, this is due to physiological characteristics, since children crawl without clothes.In general, vulgar papillomas are found in groups, but a prolonged existence of a single element is possible for several years.Immunodeficiency conditions and general diseases contribute to the spread of the process, in isolated cases, vulgar papilloma is malignant.
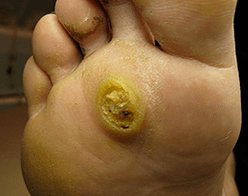
The causal agents of papillomas are Papc 1.2.4.A few months after infection in the sole skin, a small bright bump appears, which has all ordinary papilloma signs and is surrounded by an outstanding edge.In some cases, small sizes subsidiaries appear around a papilloma, which externally resemble bubbles.Then mosaic papillomatosis is diagnosed.
Papillomas in plants are often painful, especially when walking.In approximately 30% of cases, they are auto -Disolution, more frequently car is observed -Processing in young children.They are often confused with calluses that appear between fingers with prolonged compression.However, calluses, unlike papillomas, have a smooth surface and retain the skin pattern.
The causal agents of flat papillomas are HPV 3.10.These papillomas of the color of the skin without changes and are seen in the form of smooth flat cones, sometimes there can be a yellowish or slightly pink tone with more rounded frequency.Multiplant papillomas are also found.Neoplasias cause pain, itching, the affected area is hyperemic.
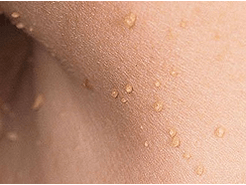
Cinematographic papillomas are diagnosed in half of those who have delivered more than 50 years about skin neoplasms, they are also called acrochords.They are located on the skin around the eyes, in the groin, in the axillary cavities and in the neck.First, a small yellowish tone appears, which increases even more and gradually becomes dense elstic formations of size up to 5-6 mm.If the acroorders are located in places where trauma is possible, then they inflate and hurt.Cinematographic papillomas are not prone to spontaneous disappearance.In patients with diagnosed threaded papillomas, straight polyps are often observed.
The HPV 13, 32 causes local epithelial hyperplasia, which is characterized by the appearance in the mucous membrane of the mouth and on the red edge of the lips of small papillary neoplasms, which rise slightly above the skin and are prone to fusion.
One of the papillomas rarely found are the papillomas of Lewandovsky-Lutz (Warty epidermodis).Most children and adolescents are sick.Sometimes, epidermodisplasia of vertiginía is the family character.It looks clinically as multiple papillomas stained red brown in the hands and feet.If papillomas are in the areas of the skin, which are more susceptible to ultraviolet radiation, then in 30% of cases they are malignant and reborn in malignant tumors with germination in neighboring tissues.
HPV, which are the pathogens of pointed condils, can be with a low, medium and high risk of oncological degeneration, therefore, by diagnosing pointed clothing, it is always necessary to carry out the PCR test.The incubation period is several weeks to several months.Since in some cases the changes are minimal, these papillomas go unnoticed.The main transmission path is sexual.The risk group includes people with immunodeficiency and often changing sexual partners.Externally, they seem to pool pink or pale gray pointed growth in the leg.
In most cases, pain, burning, itching, irritation when touching and friction with underwear, often injured and bleeding are observed.They are located on the eve of the vagina, on small lips, less frequently, there are spicy condylomas in the vagina and cervix.In men, the urethra hole is affected.The damage zone depends on sexual behavior in this way, on people who practice anal contacts, pointed condylomas are in the perineum and in the perianal area.In some cases, pointed condylomas are diagnosed in the oral mucosa and on the red edge of the lips, which is again associated with the characteristics of sexual activity.
Youth papillomas of the larynx are rarely registered, are caused by HPV 6.11;For the most part, children under five are sick.The infection occurs during childbirth, when the woman at labor has papillomas in the vagina and the child while passes through the birth channel, breathes prematurely.The disease is characterized by papillary growth in vocal packages, which leads to the difficulty of air circulation and speech disorders.
Papillomas diagnosis
The diagnosis of papillomas is carried out by a dermatologist or veneraologist.Due to the large number of types of viruses, it has its own characteristics.It is possible to make a precise diagnosis based on a visual inspection only in the classic case of pointed warts, but this does not provide precise information about the type of virus and their oncogenicity.Therefore, in case of suspicion of the papillomatous nature of neoplasms, they resort to the PCR diagnoses of the virus DNA.
The PCR diagnosis not only allows the presence of human papilloma to be confirmed in the body and determine its type, but also to diagnose how many viruses are in the body at the time of the analysis.This has a diagnostic value, since it knows the percentage of the virus content and its type, you can determine the approximate periods of infection and identify contact people to examine and prescribe preventive therapy.PCR diagnosis also provides information on whether papillomas have a chronic course or are a consequence of a simultaneous decrease in immunity.Thanks to such data, appropriate therapy can be prescribed.
If the only method of treatment is the elimination of papillomas, then, in parallel to surgery, a biopsy for cytological research is carried out.A histological examination of the papillomas tissue provides more precise results, since the exam is subject to the cells, so the correct location of their layers and the structural characteristics of the tissue.This provides reliable results on the degree of changes in the body and about the probability of malignancy, since long -term and non -anequal papillomies lead more frequently to cancer than HPV detected with a high degree of oncoris.
As a general rule, the PCR diagnosis is a nature detection and, if the analysis confirms the presence of the virus, an additional study is carried out.
Papilloma treatment
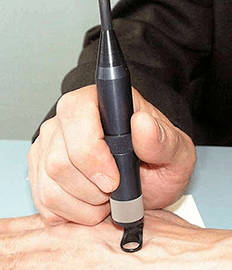
The papillomas treatment regime in each case is selected individually.If HPV is detected during diagnosis, but there are still no clinical manifestations, cytostatic prescribes preventive therapy.It is quite effective and allows you to "throw" the virus for several years.Patients who are HPV carriers are recommended to periodically perform the PCR exam and use barrier contraception means, so as not danger the human papillomava infection with their partner.
The inozina Pranobex is a drug for the treatment of papillomas of the group of antiviral agents, which suppresses the reproduction of viruses.It is one of the most preferred, since it has immunomodulatory properties.The indications for their use are diagnosed papillomas with a combination of other viral infections, such as cytomegalovirus, measles and paper infections.The presence of a herpes virus, chronic viral hepatitis and immunodeficiency also requires the inclusion of isoprinosine in the treatment regime.Since Papilloma therapy is long, Papillo Pranobex should only be taken under the supervision of a doctor, since it is necessary to control laboratory indicators.The use of immunomodulators and vitamin courses shows all patients with HPV.
If there are manifestations of HPV in the skin and mucous membranes, then, depending on the location and symptoms, they resort to papilloma chriodstruction, electrocoagulation or the elimination of the papile laser.It is possible to use another modern method of surgical treatment: removal of papillomas with radio waves.If the papilloma has signs of malignancy, then the split is carried out with a scalpel of the affected area with the capture of healthy tissues.
It should be taken into account that the elimination of papillomas does not lead to a complete recovery, since today there are no drugs that are detailed in HPV.Therefore, patients with diagnosed papillomas previously should be submitted periodically to the exam and perform antiviral therapy courses.
Since HPV is mainly transmitted sexually, the only prevention of papillomas is the barrier contraception method.When planning pregnancy, it is necessary to diagnose and, if necessary, then the treatment of the virus to reduce the probability of child infection during childbirth and in the first years of life.


















